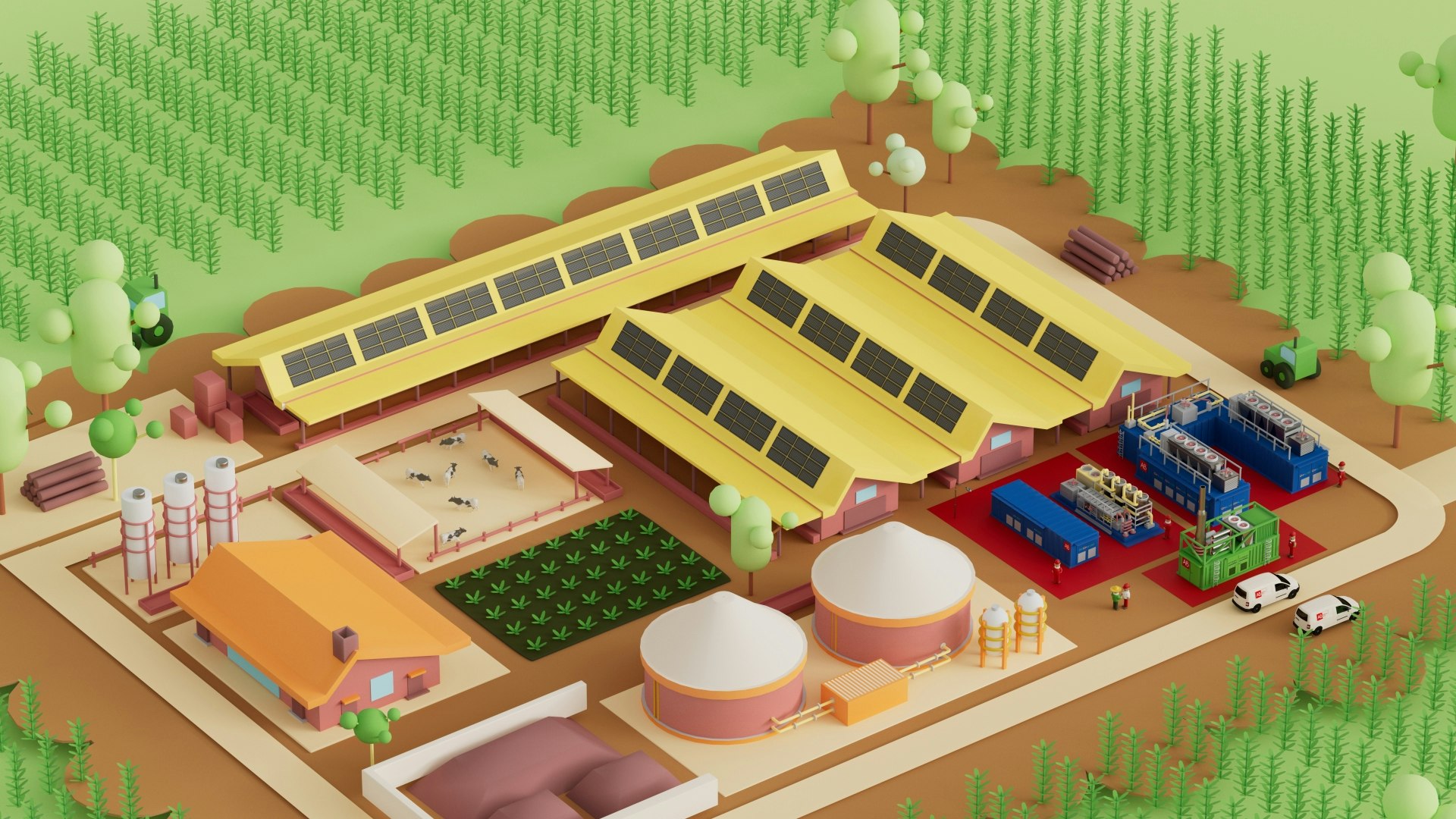
Biomethane is a renewable gas produced from biogas. Considered in all respects an alternative and clean fuel comparable to methane gas, biomethane is obtained by subjecting the raw biogas to a purification process called upgrading.
At a global level, awareness of the importance of biomethane in terms of the ongoing energy and ecological transition is increasing. Biomethane, generated from waste or scrap, is in fact a totally renewable fuel, able to guarantee a greater capacity for energy self-sufficiency and more competitive prices.
What is biomethane?
Biomethane is a fuel obtained from the purification of raw biogas, in turn obtained from the exploitation of sustainable raw materials: agricultural biomass (by-products, agricultural waste and animal waste), agro-industrial waste (waste from the processing of the food chain) or the organic fraction of municipal solid waste (FORSU).
Once the biogas has been upgraded to biomethane, it must be refined in order to eliminate the components not suitable for its use. Following the appropriate chemical-physical treatments, biomethane becomes suitable for the introduction of natural gas into the grid or for transport in cryogenic tankers.
Biomethane and sustainability
As it is produced from livestock waste, agro-industrial waste, organic waste and agricultural biomass, biomethane is in all respects a renewable and sustainable source of energy.
Circular economy: in addition to reducing emissions into the atmosphere, biomethane is carbon neutral, that is, it fully compensates the emissions produced to generate it, returning organic matter to the soil;
Decarbonisation: if supported at the legislative level, by 2030 biomethane production plants could contribute to the supply of 10% of all gas consumed in the European Union, reducing the burden from fossil sources;
Energy independence: this is a solution that can significantly contribute to the energy and ecological transition, with important implications in terms of independence from foreign energy supplies.
Biomethane for companies
Biomethane is an excellent investment opportunity for many companies in the agricultural and industrial sector which, in addition to committing to increasing the sustainability of their production, have the opportunity to generate profit and increase the level of competitiveness. According to a recent report by the European Biogas Association, biomethane has shown to be 30% cheaper than natural gas.
To become a conscious producer of biomethane it is necessary to consider different aspects and follow a well-defined process. Production can take place through the conversion of an existing plant or through the commissioning of a new plant. In both cases there are procedures to be followed to start production and obtain incentives.
Biomethane plant
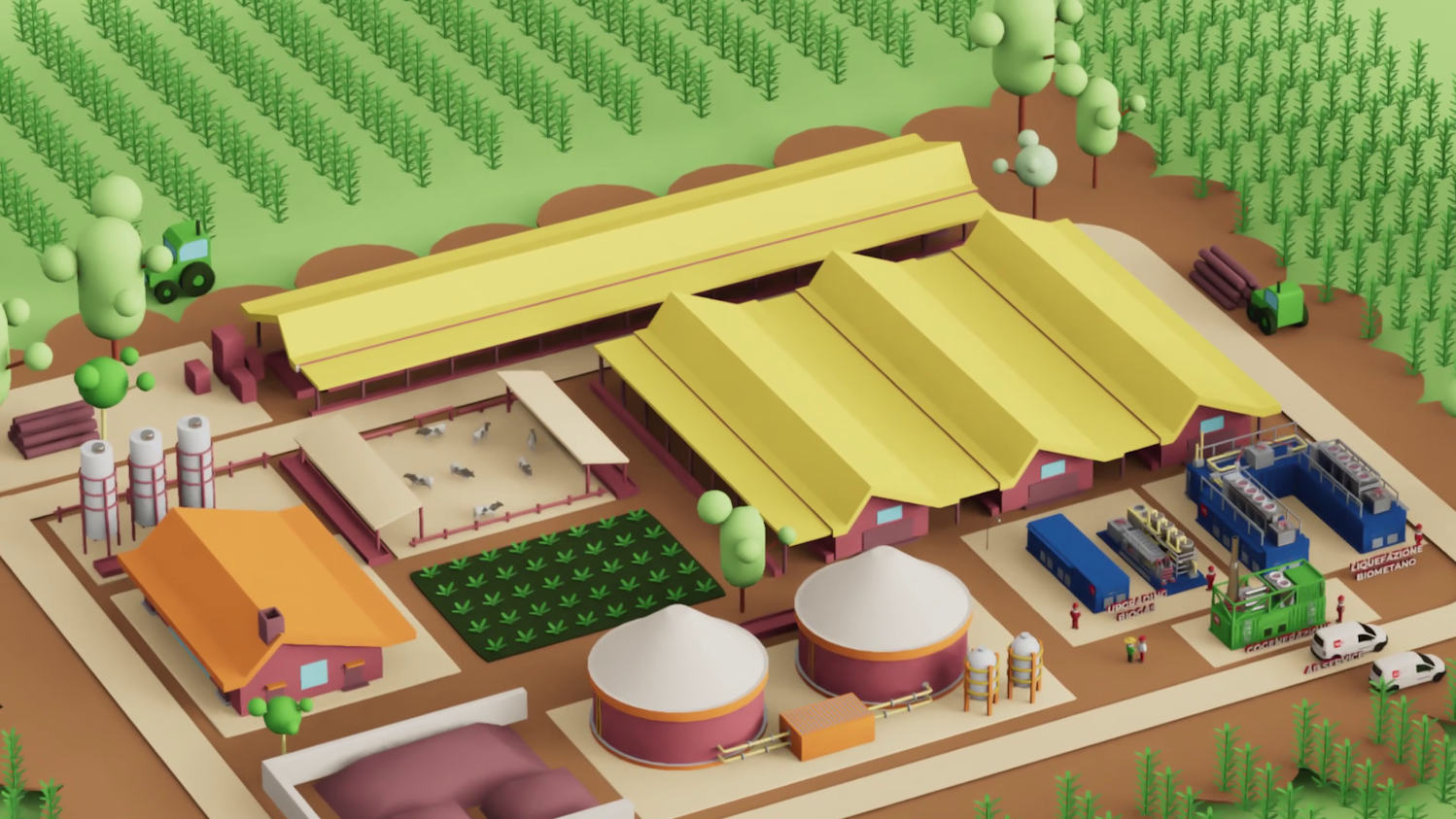
A biomethane plant integrates different technologies. In addition to the anaerobic digestion system, which produces biogas from the transformation of biomass, we also find:
A biogas purification and pretreatment system;
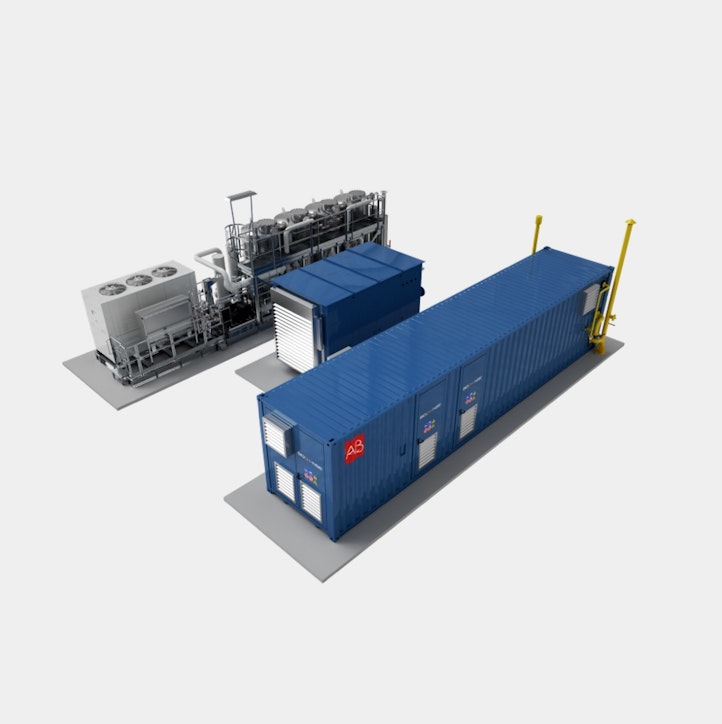
An upgrading system: this is a treatment aimed at removing CO₂ from raw biogas. Among the different upgrading technologies for biomethane available, the most popular and best-performing is the membrane system. In this case, the biomethane produced is suitable for introduction into the distribution networks;
A liquefaction system (where necessary): where logistical constraints do not make it possible to connect to the natural gas network, the solution is liquid biomethane. Liquefied biomethane is not only easily transportable but also guarantees greater efficiency when used as a fuel.
In addition to the biomethane plant, it is possible to take advantage of supporting technologies, which guarantee numerous advantages, especially in terms of optimisation: efficient and sustainable self-consumption, maximisation of plant production, dialogue and compatibility and economic savings.
RTO (waste gas treatment): the residual methane in the off-gas plays a crucial role in terms of sustainability and, for this reason, requires a specific treatment;
CO₂ liquefaction: the CO₂ liquefaction system allows the purification and liquefaction of the carbon dioxide-rich gas from the biogas upgrading system, in order to obtain liquid CO₂ suitable for food and industrial use;
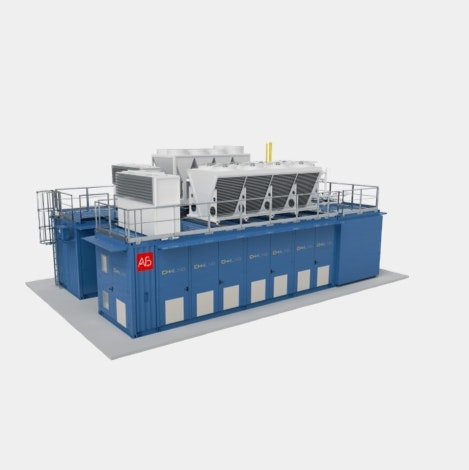
Cogeneration solutions: aimed at covering the electrical and thermal needs of the plant, a cogeneration plant powered by biogas can produce fully renewable energy;
Photovoltaic system: the installation of photovoltaic panels, modulated by the cogenerator, can help optimise the coverage of the system’s electrical needs.

Plant feasibility study
The feasibility study is the first and most important step in the production of biomethane, as it is necessary to define the correct plant sizing, energy performance and return on investment time. At a detailed level, there are three steps to be taken to assess the actual feasibility of the system.
The first step is to carry out a preliminary design of the plant to be followed by the economic and financial business plan. At this stage, it is important to have evaluated the technologies to be installed and to have selected the relevant technology partners;
The next step is to proceed with the submission of the request for authorisation for the conversion or construction of the plant, relying on competent technicians.
Finally, it is necessary to start a dialogue with credit institutions to verify the financing eligibility of the initiative.
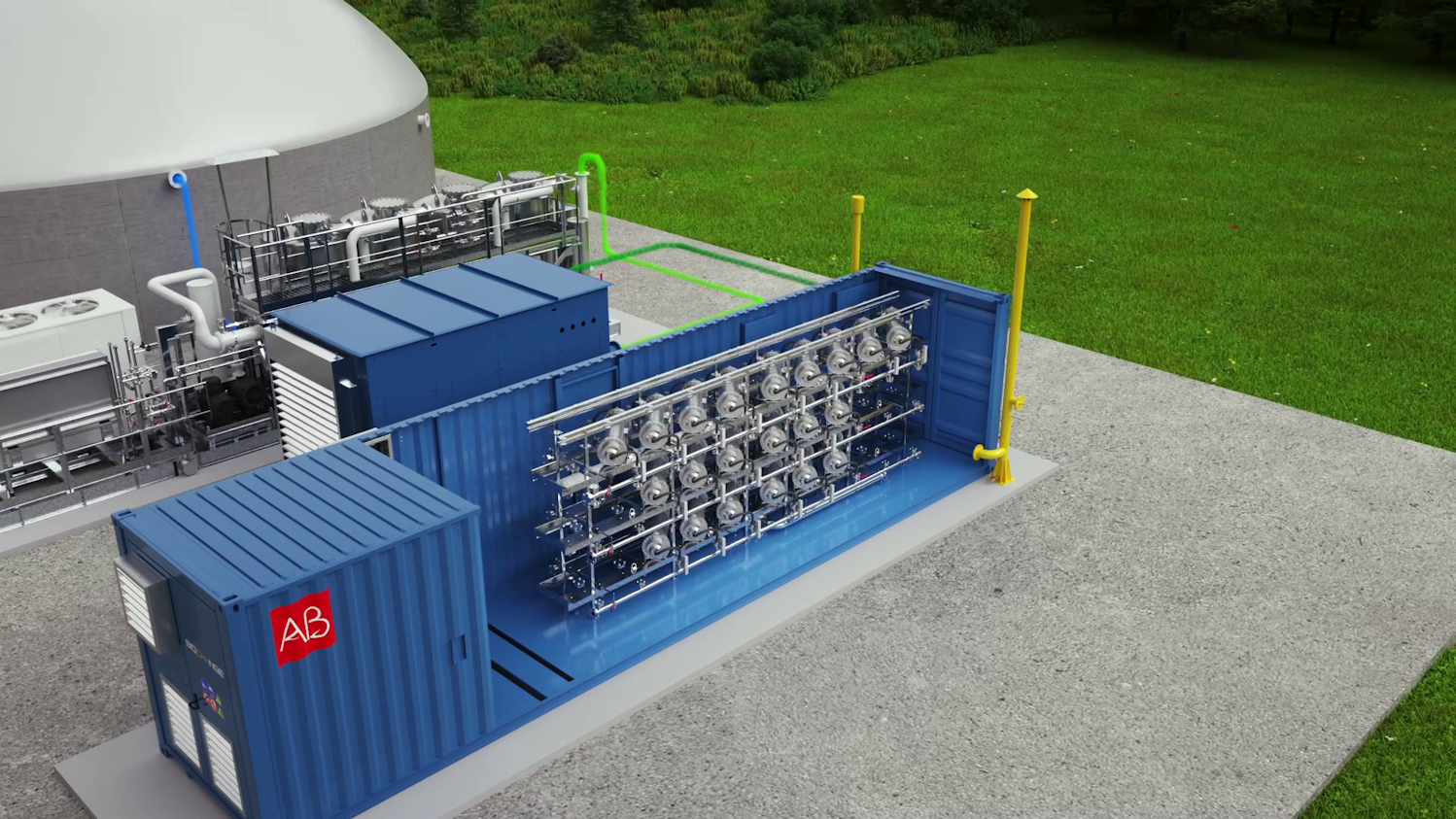
Upgrading: the compressed biomethane production process
Biogas upgrading is the treatment aimed at removing CO₂ from raw biogas to obtain compressed biomethane. Among the different upgrading technologies for biomethane available, the most popular and best-performing is the membrane system, characterised by a selective permeability beneficial for the CH₄ and CO₂ separation. The upgrading process is divided into three stages:
Biogas filtration: the upgrading process begins with the purification of the biogas coming from the anaerobic digester for the removal of water, pollutants and compression. The filtered and dehumidified gas is compressed, cooled and sent to the next treatment phase;
Purification of pollutants (H₂S, VOCs): the biogas is purified from pollutants through a bed of activated carbon. In the "Lead-Lag" version, the configuration of the carbon includes a series of valves that allow the reversal of flows, the bypassing and the sectioning of the single filter, thus guaranteeing flexibility, reliability and continuity of service;
Upgrading: the pre-treated and purified biogas is ready for the actual upgrading process, in other words the separation of methane from carbon dioxide. The process is optimised in terms of consumption and makes it possible to obtain a biomethane with the desired characteristics for the different uses. Biomethane is produced at a pressure ranging from 7 to 15 bar, to minimise consumption and facilitate its introduction into distribution networks.
The upgrading process is completed by a series of preparatory options for feeding into the grid and other accessories to accompany the operation of the plant:
Desulfurisation system and washing tower: Upstream of the biogas treatment, a desulphurisation system is available to lower the hydrogen sulphide content and a washing tower to reduce the ammonia content;
Oxygen concentration system: in case of low concentration of oxygen in the biogas, an oxygen concentration system from ambient air makes it possible to supply the necessary quantity so that the chemical reactions of contaminant adsorption by activated carbon take place correctly;
Regenerative thermal oxidisers (RTO): in order to eliminate even the small percentages of methane remaining in the off-gas;
Booster compressor: A booster compressor can be supplied to reach the pressure required by the transport networks. Before being fed into the grid, the REMI cabin measures the flow rate of the biomethane and analyses its quality.
The main advantages and benefits of membrane upgrading technology include:
Simple upgrading process
High efficiency and low consumption
High scalability and flexibility
Affordable plant cost
Liquefaction: the process of producing liquid biomethane
Connection to the natural gas grid is not always possible. Where logistical constraints exist, the solution is liquid biomethane (bio-LNG). Liquefied biomethane, in fact, is not only easily transportable but, thanks to its density, which is three times higher than that of compressed natural gas, it guarantees greater efficiency when used as a fuel.
The liquefaction of biomethane is a complex process, which consists of cooling and compressing the gaseous biomethane at very low temperatures. The liquefaction process is based on an integrated, low operating pressure cryogenic process, divided into 3 phases: treatment, liquefaction and storage.
Treatment: in the first part of the process, the TSA (Temperature Swing Adsorption) purification system lowers the moisture and CO₂ contents through molecular sieve filters;
Liquefaction: through several cooling stages, the biomethane under pressure passes into the liquid state and is made available under conditions of < -142 °C and 3 moisture or at lower temperatures and pressures. The heart of the process is the cryo-cooler, relying on the Stirling Cryogenics technology, which is an alternative refrigeration machine that works by compressing and expanding helium in a closed cycle;
Storage: the bio-LNG is conveyed into a transfer tank, where the desired pressure and temperature conditions of the final product are reached.
System maintenance
Whatever the type of biomethane plant, it must be protected from failures and breakdowns, thanks to a coordinated and planned series of interventions to maximise its usability. The advantages of an integrated service are evident right from the time the plant is installed: specialists will in fact facilitate the commissioning of the plant, follow and optimise the start-up phase.
In addition to on-site assistance and an emergency response activity, the integrated service monitors all the systems 24/7, 365 days a year, with the activation of the diagnostics and remote assistance service. The service can also offer training and continuous updating courses to ensure the best operation to the customer and correct management and maintenance of the plant.
The plant service and maintenance agreements are designed and customised according to the customer's needs, to meet their requirements, ensure high returns throughout the life of the plant and guarantee greater predictability of operating costs.
Conclusions
The future of biomethane plants
In Italy, as well as outside national borders, the biomethane sector is taking on an increasingly important role in contributing to the energy transition path and to the development of renewable energy. Biogas and biomethane farms therefore are two key assets to help promote the circular economy, accompany a sustainable green transition and contribute to energy security and independence.
The interventions introduced with the National Recovery and Resilience Plan (PNRR) constitute an important drive towards an agriculture 4.0 model that guarantees optimisation and greater efficiency of production processes, less use of chemicals and protection of the soil. In this context, biogas and biomethane represent a significant strategic heritage to respond to the challenge of renewable energy, guarantee food autonomy, care for the territory and climate protection.
AB technologies for the production of biomethane
Since 1981 AB has been at the side of companies that want to increase their competitiveness, saving energy and limiting emissions into the environment. The Group is characterised by competence, production capacity and a high quality service, with the aim of providing customers with the very best energy sustainability solutions.
AB is the only partner to guarantee your company all the advantages of biomethane. With AB, in fact, companies can develop and implement a complete and sustainable energy system, combining biogas upgrading, biomethane and CO₂ liquefaction, cogeneration and photovoltaic technologies, supported by a full range of services, extending from feasibility studies to plant maintenance.
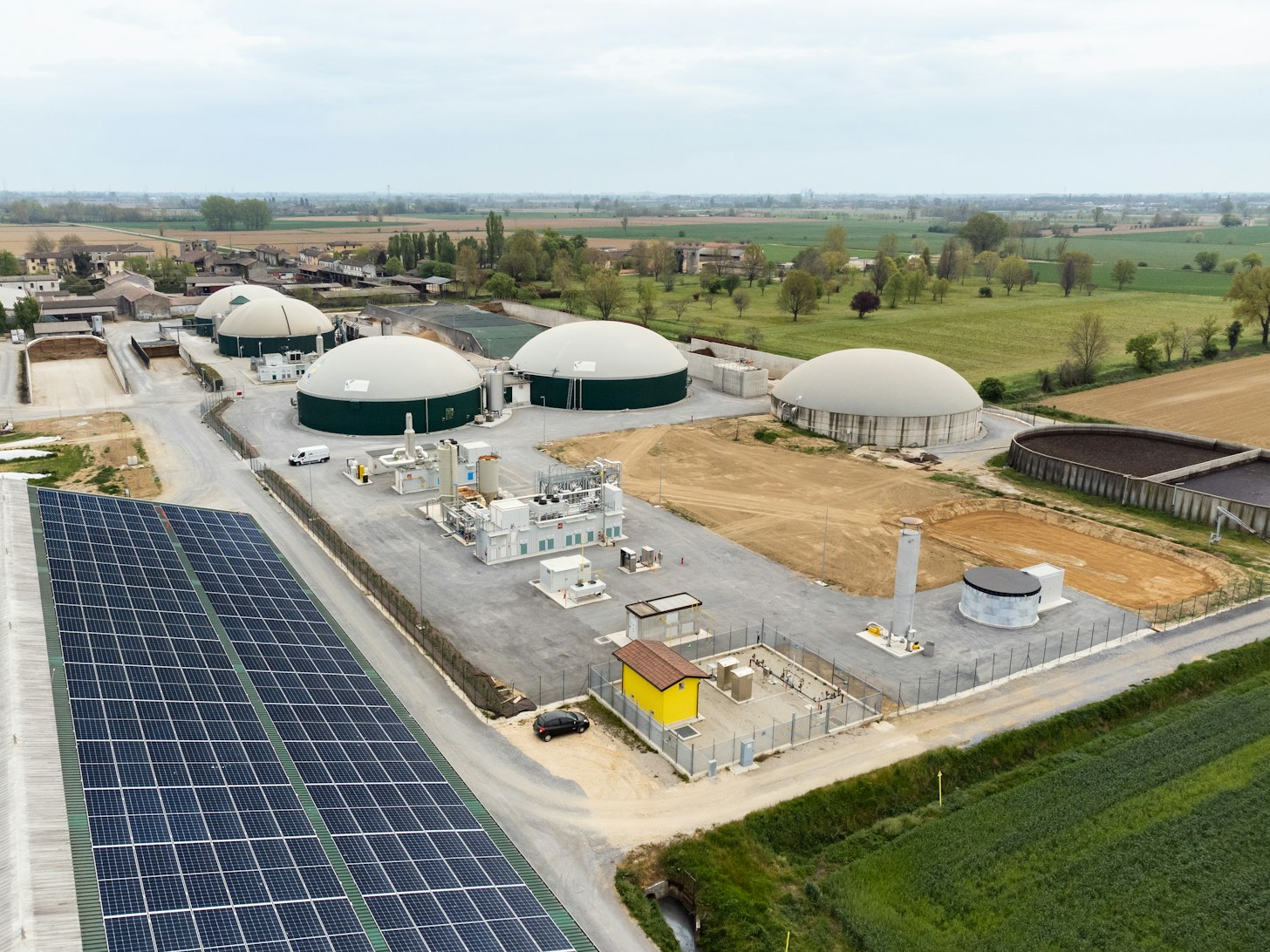
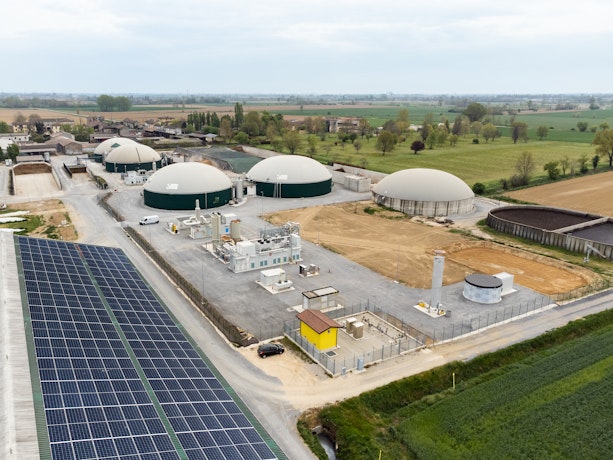


SOC. AGRICOLA PALAZZETTO

MOTTA ENERGIA e EBS

LA CASTELLANA
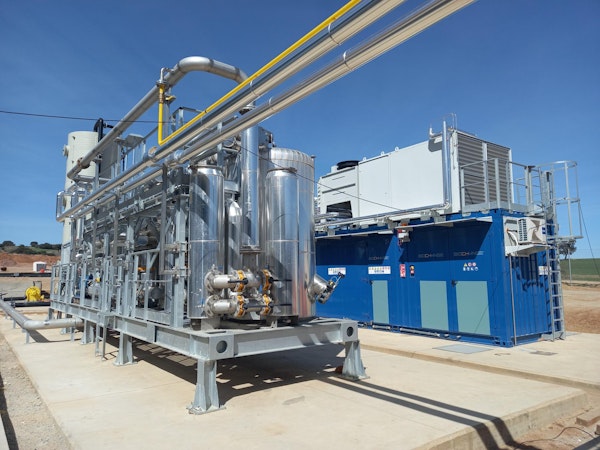

BIOLVEGAS

POUCHIOU ENERGIE

